
In Wireshark menu, click on “capture” and then select “capture filters”. Then log out and log in again to let the usermod change to take effect or simply reboot your system: $ sudo reboot 2) Configure Wireshark filter Then add your user to a “wireshark” group: $ sudo usermod -a -G wireshark "$USER"
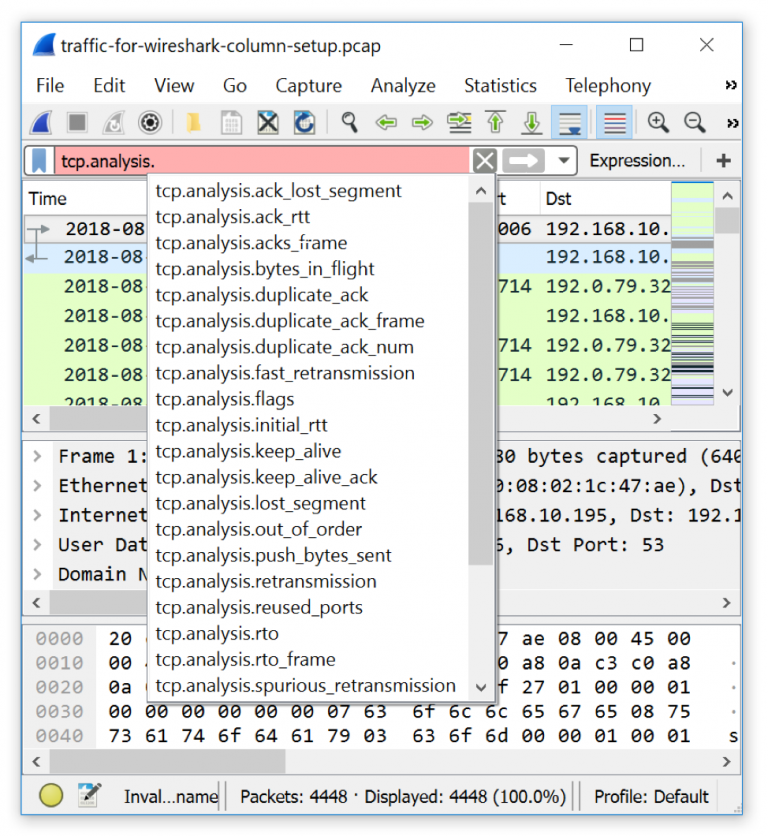

On Fedora you install Wireshark by: $ sudo dnf install wireshark We will configure MikroTik router to stream captured packets to our computer where we will be capturing and analyzing them with Wireshark. Where and are network specifiers, such as 10.0.0.0/8.Today, I will describe how to analyze traffic passing through a MikroTik router on your local machine with Wireshark. You can look for external recursive queries with a filter such as udp port 53 and (udp & 1 = 1) and src net not and src net not
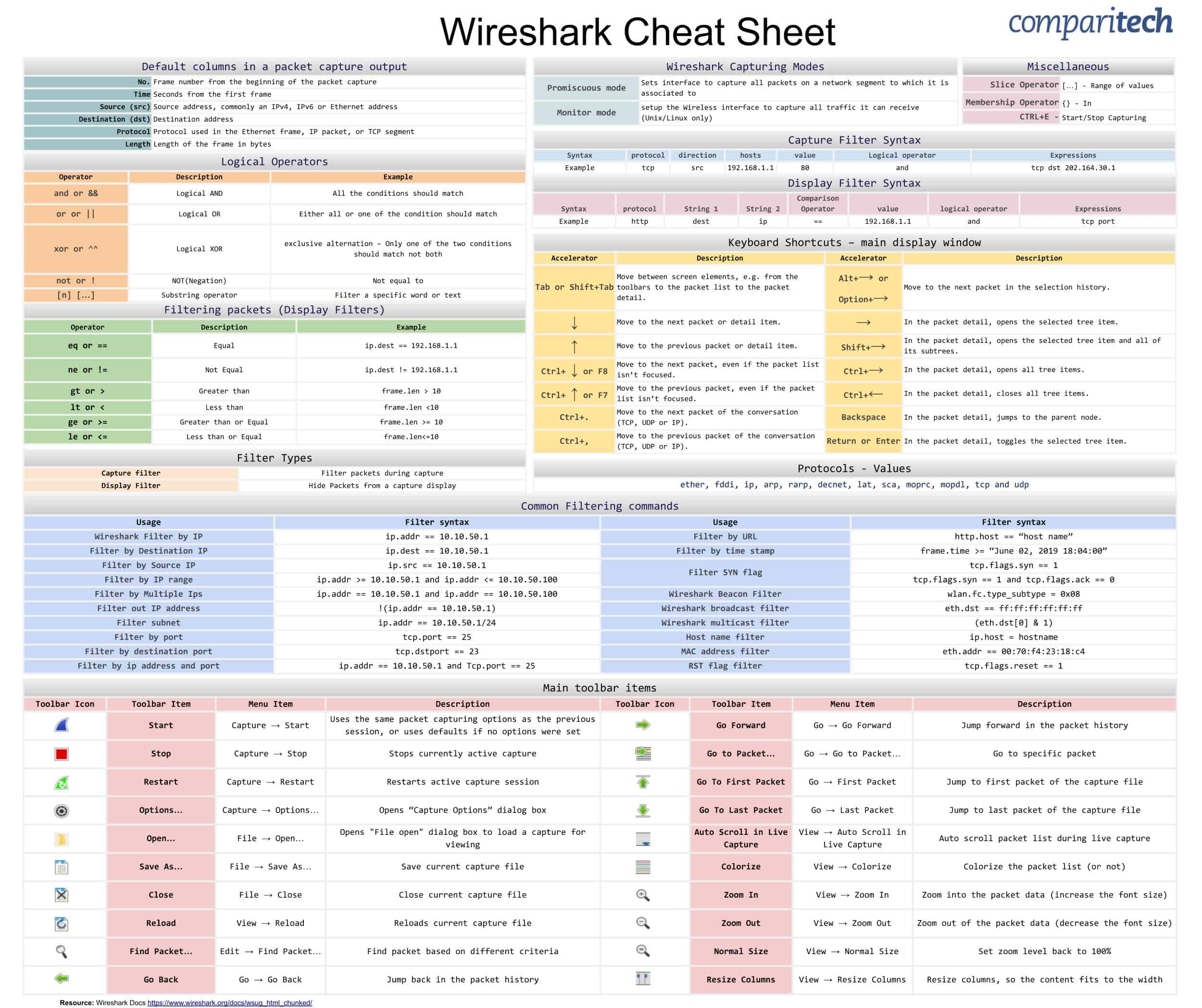
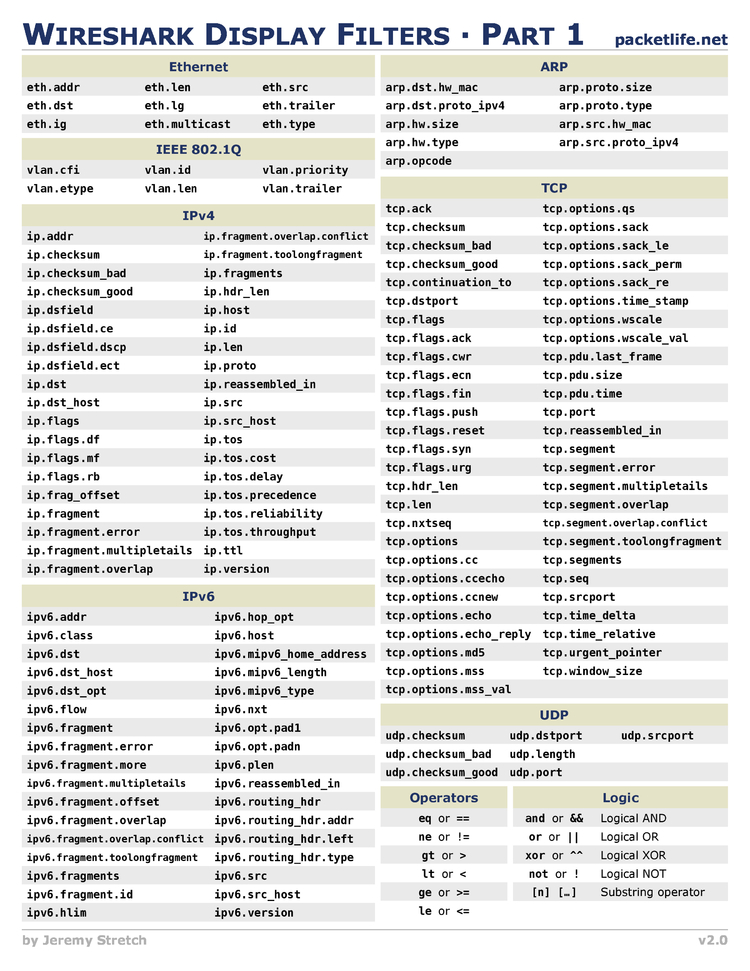
On many systems, you can say "port domain" rather than "port 53".ĭNS servers that allow recursive queries from external networks can be used to perform denial of service (DDoS) attacks. However, DNS traffic normally goes to or from port 53, and traffic to and from that port is normally DNS traffic, so you can filter on that port number.Ĭapture only traffic to and from port 53: port 53 You cannot directly filter DNS protocols while capturing if they are going to or from arbitrary ports. Show only the DNS based traffic: dns Capture Filter Display FilterĪ complete list of DNS display filter fields can be found in the display filter reference The SampleCaptures has many DNS capture files. TCP_Reassembly has to be enabled for this feature to work. As you might have guessed, this takes a DNS request or reply that has been split across multiple TCP segments and reassembles it back into one message. The DNS dissector has one preference: "Reassemble DNS messages spanning multiple TCP segments". Also add info of additional Wireshark features where appropriate, like special statistics of this protocol. XXX - Add example traffic here (as plain text or Wireshark screenshot). The well known TCP/UDP port for DNS traffic is 53.
HistoryĭNS was invented in 1982-1983 by Paul Mockapteris and Jon Postel. DNS is the system used to resolve store information about domain names including IP addresses, mail servers, and other information.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
